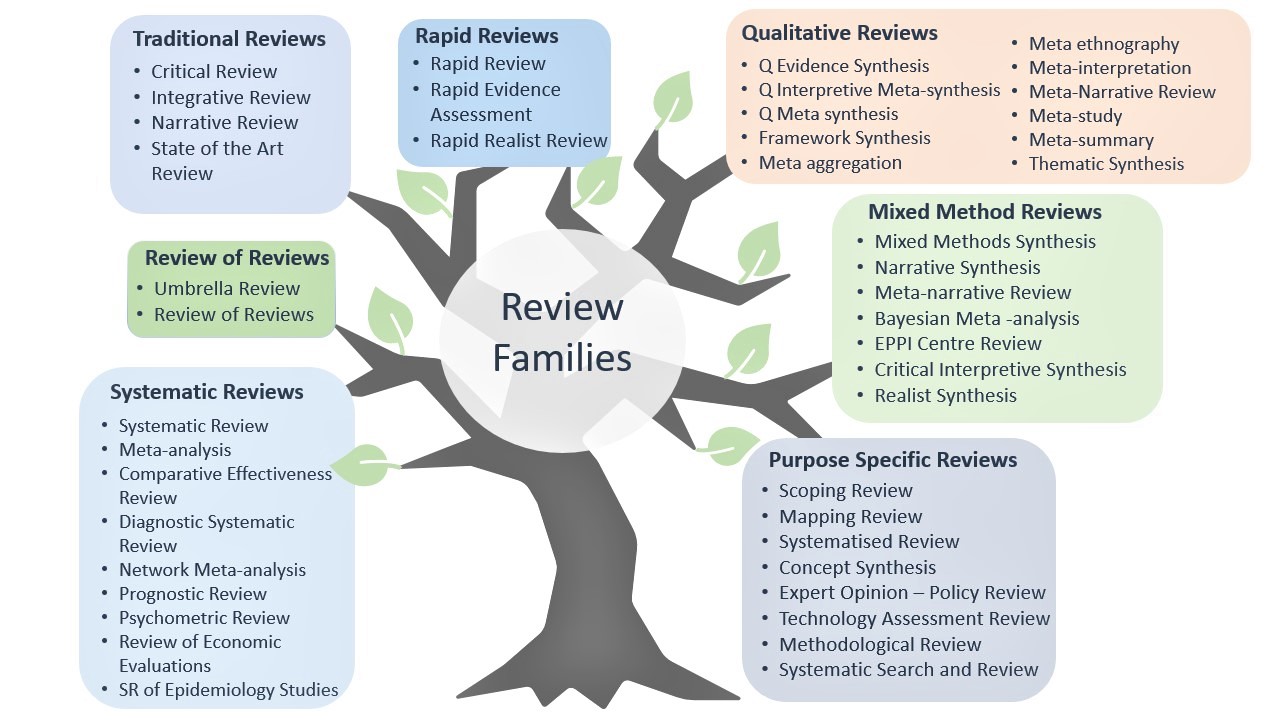
Image from: Birkic, V., Celeste, T., & Cochrane, L. (2020). Which review is that? A guide to review types, Available from https://unimelb.libguides.com/whichreview. Shared under a CC BY ND 4.0 licence
| Review type | Description & purpose |
Literature search | Quality appraisal | Analysis methods | Recommended timeframe* | Reviewers required | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Comprehensive evidence synthesis, considered the gold standard review with a focus on high level evidence (often randomised controlled trials, but this depends on the question type). May be useful for clinical decision-making, determining best practice The Cochrane Collaboration is considered the eminent organisation for systematic reviews. Note: not all systematic reviews include meta-analyses |
Comprehensive | Included - this may determine inclusion/exclusion | What is known: recommendations for practice or what remains unknown: uncertainty around findings, recommendations for future research | 9-12+ months | at least 2 |
Narrow scope of question limits insights on broader topic.
|
|
|
Exploratory review. May assist with determining areas for new research or the usefulness of a future systematic review |
Completeness determined by time/scope restraints | No formal quality assessment | Characterises quantity and quality of literature perhaps by study design and other key features | 6-12+ months | at least 2 |
Difficulty in establishing boundaries due to wide scope. Difficult to interpret results due to lack of quality assessment. Does not synthesise results. |
|
|
Rapid evidence synthesis. May assist with determining best practice. |
Comprehensive Completeness determined by time/scope restraints? |
Included - this may determine inclusion/exclusion | What is known: recommendations for practice or what remains unknown: uncertainty around findings, recommendations for future research | 1 - 6 months | at least 1 |
Search not as comprehensive. Limited time frame may introduce bias. Only one reviewer may cause possible non-blinded appraisal and selection. Omitting components of the review process may cause limitations and potential biases. Interpretation of the findings may be limited or cautious. |
|
|
Aggregates and evaluates both experimental and non-experimental data to determine best practice. May assist where diverse methodologies are required to answer a question, or where empirical evidence may not exist. |
Comprehensive | Included - this may determine inclusion/exclusion | What is known: recommendations for practice or what remains unknown: uncertainty around findings, recommendations for future research | 12+ months | at least 2-3 | |
|
|
Systematic review of other systematic reviews Usually used for best practice for treatment. |
Included - this may determine inclusion/exclusion | What is known: recommendations for practice or what remains unknown: uncertainty around findings, recommendations for future research | 9-12+ months | at least 2 |
Must include the re-synthesis of data. Only includes systematic reviews and meta-analyses, does not include other study types. Requires a systematic review expert to critically appraise systematic reviews. |
|
|
|
Strictly speaking not a review, but is usually developed from or within a systematic review. Determines the effectiveness of interventions by applying statistical analysis to the combined results of individual studies. |
Comprehensive | Included - this may determine inclusion/exclusion | What is known: recommendations for practice or what remains unknown: uncertainty around findings, recommendations for future research | 12 - 24 months | at least 2-3 |
Requires specialist statistical expertise and software. Assumes that all interventions are equally applicable to all populations and contexts of the studies included. May introduce study selection bias.
|
|
|
An interpretive synthesis of qualitative data which provides new insights into the research. | Comprehensive | Included - this may determine inclusion/exclusion | What is known: recommendations for practice or what remains unknown: uncertainty around findings, recommendations for future research | NA | NA |
Only appropriate for high-quality qualitative studies Selection of review type may not be possible until studies selected. Requires significant methodological skill and experience with qualitative methods. May take time to engage with the evidence and develop theory. Requires further interpretation by policy makers and practitioners. |
|
|
Increase self-knowledge of an area, provide a broad overview or identify gaps in the literature. May be used as background for research. |
May or may not be comprehensive | May or may not include | May be chronological, conceptual, thematic etc. | 1 week - 1 month | 1 |
No data about author's purpose or agenda. No explicit analysis of data. Possible study selection bias. |
*timeframe may vary from this guide, depending on the number of eligible articles included in the review and other demands on the reviewers' time.
We acknowledge the Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples as the first inhabitants of the nation and acknowledge Traditional Owners of the lands where our staff and students, live, learn and work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-SA) 4.0 International License, unless otherwise noted. Content from this Guide should be attributed to James Cook University Library. This does not apply to images, third party material (seek permission from the original owner) or any logos or insignia belonging to JCU or other bodies, which remain All Rights Reserved.